Table of Contents
PowerShell 7 is the latest cross-platform automation and configuration management framework developed by Microsoft. It extends the functionality of the traditional Windows PowerShell, offering enhanced performance, expanded features, and compatibility with different operating systems (Windows, macOS, and Linux). Whether you’re deploying multiple devices within an organization or setting up a few personal machines, installing or uninstalling PowerShell 7 silently and automatically on Windows computers can save time and effort, particularly for IT administrators. This guide will outline several detailed methods to silently install or uninstall PowerShell 7, ensuring the process is seamless and automated without requiring user interaction.
| 1 | 2 |
|---|---|
| Software Name | PowerShell 7 |
| Architecture | 64-bit |
| Software Version | 7.5.0 |
| Download (.msi) | PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi |
| Silent Installation | msiexec.exe /i "PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi" /qn |
| Silent Uninstallation | msiexec.exe /X "{D012DCD1-67EA-4627-938F-19FD677FC03A}" /qn |
What is Silent Installation?
Silent installation refers to installing software without showing any prompts, dialogs, or requiring user interaction. This is particularly useful for IT administrators, automated scripts, or bulk deployments. It brings a host of benefits that streamline software deployment. Here’s a concise look at why silent installation is advantageous:
- Time and effort savings: Automate the installation process, eliminating manual intervention and saving valuable time and effort.
- User-friendly experience: Minimize interruptions and prompts, providing a seamless installation process for users, and enhancing productivity.
- Customization and control: Tailor the installation to your organization’s needs by specifying parameters such as location, language, and components.
- Scalability and efficiency: Easily deploy software on a large scale, saving time and ensuring a streamlined installation process.
Download link for the PowerShell 7 installer
The initial step involves locating the download link for the installer. The Windows Package Manager can be used to find this link. It is a comprehensive package management solution that comes pre-installed on Windows 11 and newer versions of Windows 10.
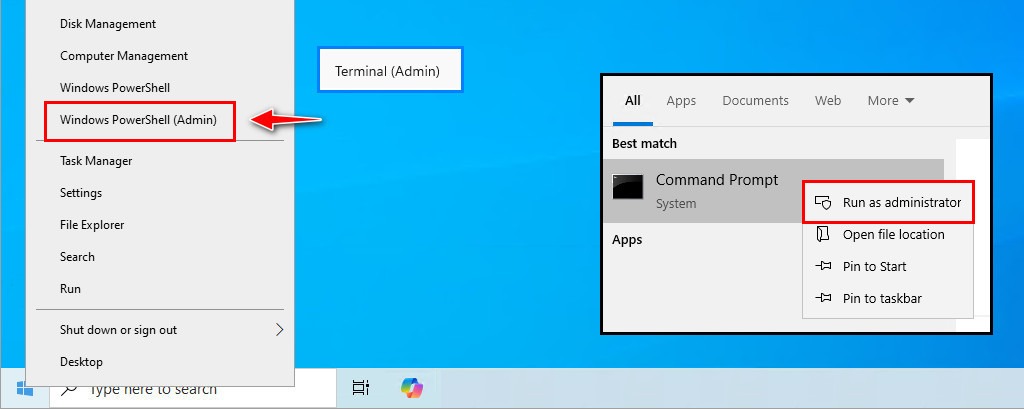
1. To obtain the direct link of PowerShell 7, first, right-click on the Windows Start icon, then selectTerminal (PowerShell) (Admin) or search for Command Prompt (CMD) and run as administrator.
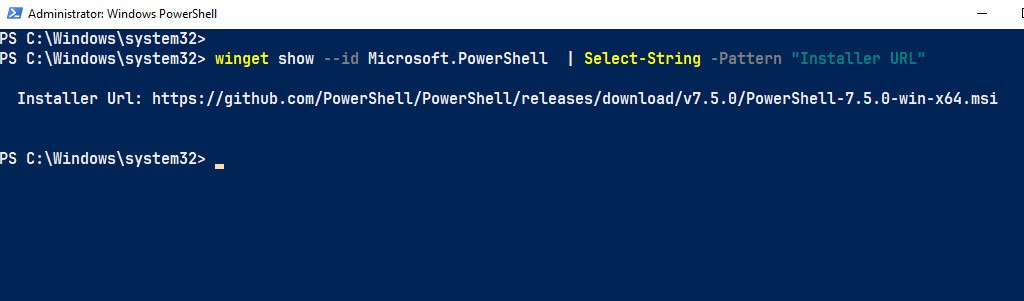
2. Please copy and execute the following command to get the official download link:
winget show --id Microsoft.PowerShell | Select-String -Pattern "Installer URL"3. You should see the output below with the direct download link for PowerShell 7. Please copy or take note of it, as we will be using it in automation scripts in the upcoming sections.
https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msiMethod 1: Single-line command installation
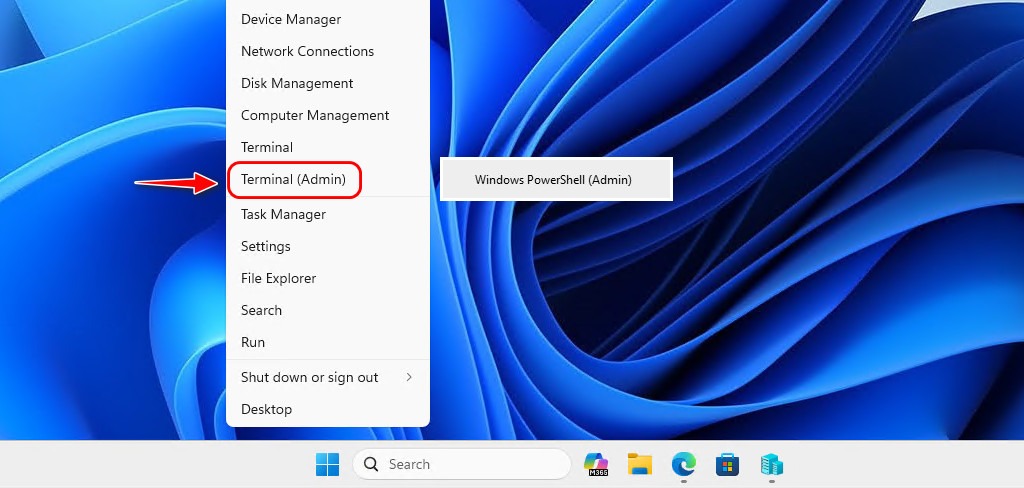
1. Once you have the download link, right-click on the Windows Start icon, then select Terminal (Admin) or PowerShell (Admin) to open an elevated PowerShell window.
2. Execute the following command to download and install PowerShell 7 silently and automatically.
msiexec /i "https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi" /qnAfter a few moments, the PowerShell 7 shortcut should appear. You will also find entries in the Start Menu, installation directory, and Programs and Features in the Control Panel.
Method 2: PowerShell Script (*.ps1)
The second method provided below is a basic PowerShell script that automates the silent installation of PowerShell 7. The script explanation:
- Declare the variables for PowerShell 7 download link and the download file path in temporary folder.
- Downloads the PowerShell 7 installer to the temporary location,
- Installs it silently using msiexec (no user prompts or UI).
- And then cleans up by deleting the temporary installer file.
# Declare variables
$DownloadLink = "https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi"
$InstallerPath = "$env:TEMP\setup.msi"
# Download and install the app
Write-Output "Downloading the installer..."
[System.Net.WebClient]::new().DownloadFile($DownloadLink, $InstallerPath)
# Install the app silently
Write-Output "Installing the app silently..."
Start-Process -FilePath "msiexec.exe" -ArgumentList "/i `"$InstallerPath`" /quiet /norestart" -Wait
Write-Output "The app has been successfully."
# Cleanup
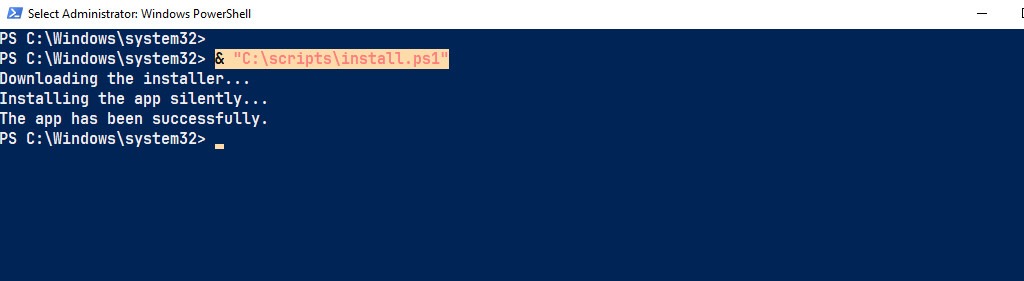
Remove-Item -Path $InstallerPath -ForceYou can copy the code snippets and paste them into a PowerShell console to execute them directly. Alternatively, you can create a PowerShell script, save it on your computer (e.g., C:\scripts\install.ps1) with a .ps1 file extension, and then run the script within a PowerShell console.
Advanced PowerShell script
The below updated script is significantly more robust, user-friendly, and reliable compared to the basic one. Features like error handling, installation verification, and detailed logging make it better suited for professional environments or scenarios where reliability is a priority. You can get the script by clicking on the button below.
# Silently Download and Install
$DownloadLink = "https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi"
$InstallerPath = "$env:TEMP\setup.msi"
# Download and install the app
Write-Output "Downloading the installer silently..."
[System.Net.WebClient]::new().DownloadFile($DownloadLink, $InstallerPath)
# Install the app silently
Write-Output "Installing the app silently..."
try {
$args = "/i `"$InstallerPath`" /quiet /norestart"
Start-Process -FilePath "msiexec.exe" -ArgumentList $args -Wait -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Output "The installation failed. Error: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
# Verify Installation
Write-Output "Verifying the installation..."
$RegKeys = @(
'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\',
'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\'
)
$AppInstalled = $RegKeys | Get-ChildItem -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue |
Get-ItemProperty -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue |
Where-Object { $_.DisplayName -like '*powershell*' }
if ($AppInstalled) {
Write-Output "The app is installed. Version: $($AppInstalled.DisplayVersion)"
} else {
Write-Output "Failed to verify installation status."
}
# Cleanup
Write-Output "Cleaning up temporary files..."
Remove-Item -Path $InstallerPath -Force -ErrorAction Stop
Write-Output "Temporary files cleaned up successfully."
Write-Output "All tasks completed successfully."# Output Advanced PowerShell script
PS C:\Windows\system32> & "C:\scripts\install.ps1"
Downloading the installer silently...
Installing the app silently...
Verifying the installation...
The app is installed. Version: 7.5.0.0
Cleaning up temporary files...
Temporary files cleaned up successfully.
All tasks completed successfully.Troubleshooting Common Issues
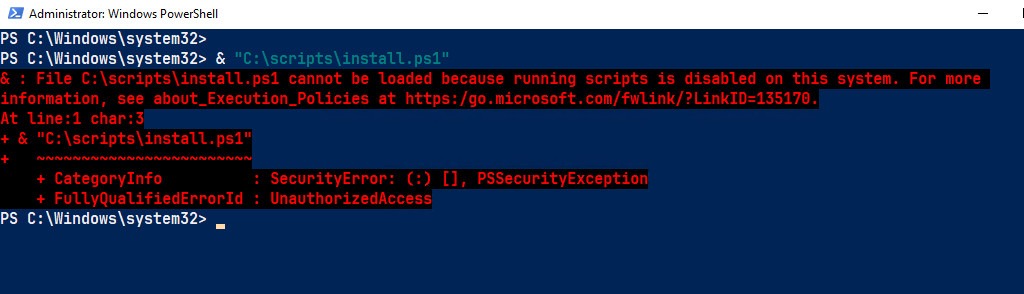
- Command Not Recognized: Please ensure that the installer file path is correct and use the absolute paths instead of relative paths.
- Permissions Error: Execute PowerShell or Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
No Silent Switch: Please double-check that you are using the correct installation switch.
Debugging with Logs: Use the /log option to generate a detailed log file:
...
try {
$args = "/i `"$InstallerPath`" /quiet /norestart /log 'C:\Logs\Install.log'"
Start-Process -FilePath "msiexec.exe" -ArgumentList $args -Wait -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
Write-Output "App installation failed. Error: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}
...Method 3: Batch Scripts (*.bat, *.cmd)
The next method is using batch script. Batch scripting is great for quick, simple, and legacy tasks, but for powerful automation workflows, PowerShell is the modern solution. Unless you have a legacy requirement, familiarity with PowerShell will generally provide much greater flexibility and capability in the long run.
Explanation of the Batch Version:
- Declare the variables for PowerShell 7 download link and the download file path in temporary folder.
- The script uses PowerShell inline (powershell -Command) to download the installer file,
- The msiexec is used to install the .msi file silently using /quiet /norestart.
- Deletes the installer file after installation to ensure no leftover files.
@echo off
setlocal
REM Define download link and target path
set "DownloadLink=https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi"
set "InstallerPath=%TEMP%\setup.msi"
echo Downloading the installer...
powershell -Command "& {[System.Net.WebClient]::new().DownloadFile('%DownloadLink%', '%InstallerPath%')}"
echo Installing the app silently...
msiexec /i "%InstallerPath%" /quiet /norestart
echo Cleaning up installer file...
del /q "%InstallerPath%"
echo The app has been successfully installed.
endlocal
pauseHow to run the batch script
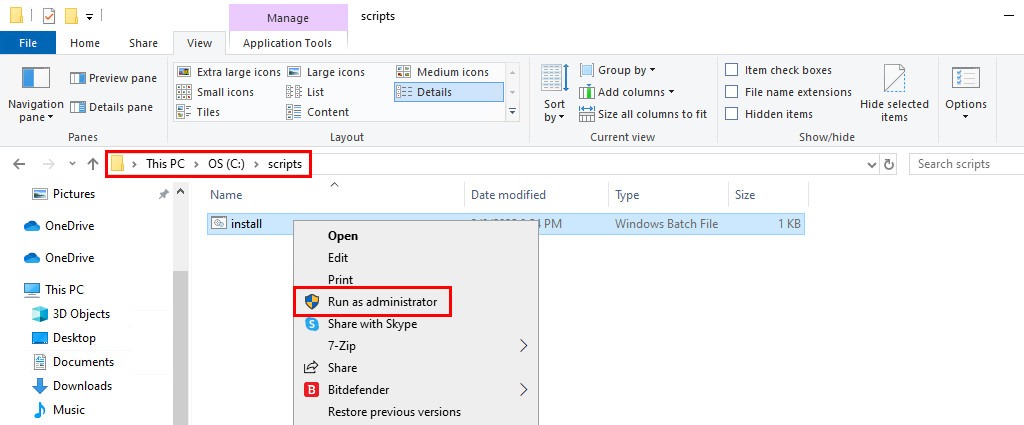
1. First, create a batch script by copying the above code snippets to a new text file and saving it with the .bat extension (e.g., “C:\scripts\install.bat”).
2. Run the batch file with administrative privileges by right-clicking on the .bat file → Run as administrator.
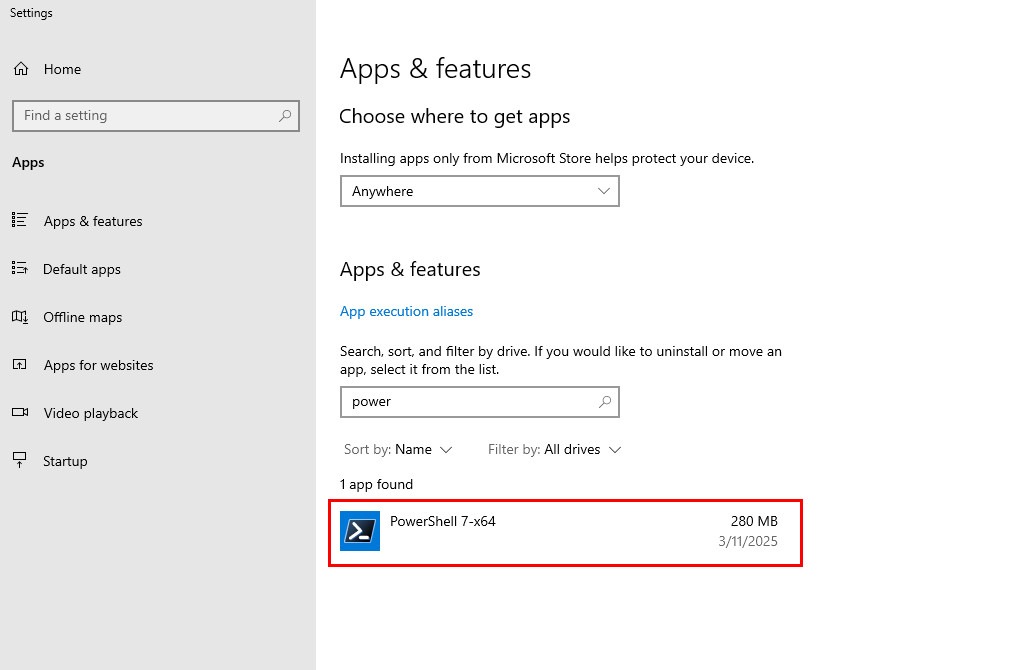
3. Verify the output to ensure that PowerShell 7 has been installed successfully.
Method 4: Install PowerShell 7 with package managers
Furthermore, on Windows computers, package managers can be used as an alternative to silently downloading and installing applications like PowerShell 7. Package managers make installations easier, faster, and repeatable, especially for IT administrators or developers managing multiple machines. Here’s an overview of using some of the most common Windows package managers to silently install PowerShell 7.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Package Manager | Ease of use | Silent install | Official support | Popular apps |
| Winget [Recommended] | Easy | Yes | Microsoft | 2000+ |
| Chocolatey | Moderate | Yes | Community-driven | 9000+ |
| Scoop | Moderate | Yes | Community-driven | 1500+ |
Install PowerShell 7 with Windows Package Manager (winget)
Winget (Windows Package Manager) is Microsoft’s official command-line package manager that ships with Windows 10 and Windows 11. It’s simple, lightweight, and perfect for managing software installations.
PS C:\Windows\system32> winget
Windows Package Manager v1.10.340
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
The winget command line utility enables installing applications and other packages from the command line.
usage: winget [<command>] [<options>]
The following commands are available:
install Installs the given package
show Shows information about a package
source Manage sources of packages
search Find and show basic info of packages
list Display installed packages
upgrade Shows and performs available upgrades
uninstall Uninstalls the given package
hash Helper to hash installer files
validate Validates a manifest file
settings Open settings or set administrator settings
features Shows the status of experimental features
export Exports a list of the installed packages
import Installs all the packages in a file
pin Manage package pins
configure Configures the system into a desired state
download Downloads the installer from a given package
repair Repairs the selected package
For more details on a specific command, pass it the help argument. [-?]To install PowerShell 7, open Windows PowerShell (Terminal) or Command Prompt (cmd) as an administrator, and then execute the following command:
winget install --id Microsoft.PowerShell --accept-package-agreements --accept-source-agreements# Output
Found PowerShell [Microsoft.PowerShell] Version 7.5.0.0
This application is licensed to you by its owner.
Microsoft is not responsible for, nor does it grant any licenses to, third-party packages.
Downloading https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi
██████████████████████████████ 107 MB / 107 MB
Successfully verified installer hash
Starting package install...
Successfully installedInstall PowerShell 7 with Chocholatey
Chocolatey is one of the most popular Windows package managers. It simplifies software installation by automating the process. The code snippets below will install the Chocolatey package manager on your system:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser -Force
irm https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1 | iex
choco feature enable -n allowGlobalConfirmation
Once Chocolatey is installed, execute the following code to install PowerShell 7 silently:
choco install powershell-core# Output is truncated
...
Chocolatey v2.4.3
Installing the following packages:
powershell-core
By installing, you accept licenses for the packages.
Downloading package from source 'https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/'
Progress: Downloading KB3118401 1.0.5... 100%
KB3118401 v1.0.5 [Approved]
KB3118401 package files install completed. Performing other installation steps.
Skipping installation because update KB3118401 does not apply to this operating system (Microsoft Windows 10 Pro).
The install of KB3118401 was successful.
Software install location not explicitly set, it could be in package or
default install location of installer.
Downloading package from source 'https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/'
Progress: Downloading powershell-core 7.5.0... 100%
powershell-core v7.5.0 [Approved]
powershell-core package files install completed. Performing other installation steps.
7.5.0
WARNING: If you started this package under PowerShell core, replacing an in-use version may be unpredictable, require multiple attempts or produce errors.
Downloading powershell-core 64 bit
from 'https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.5.0/PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi'
Progress: 100% - Completed download of C:\Users\chris\AppData\Local\Temp\chocolatey\powershell-core\7.5.0\PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi (107.82 MB).
Download of PowerShell-7.5.0-win-x64.msi (107.82 MB) completed.
Hashes match.
Installing powershell-core...
powershell-core has been installed.Uninstall PowerShell 7 Silently
If the application is no longer required, it can also be uninstalled silently. Below are several methods to remove it depending on how it was installed.
Using PowerShell to uninstall silently
Below is a one-line command to uninstall PowerShell 7 silently and automatically. The command can be executed in both PowerShell and Command Prompt (CMD).
msiexec.exe /x "{D012DCD1-67EA-4627-938F-19FD677FC03A}" /qnAlternatively, the following code provides an advanced script to uninstall PowerShell 7 with error handling.
# Unstall Silently
Write-Output "Uninstalling the app silently..."
try {
$args = "/x {D012DCD1-67EA-4627-938F-19FD677FC03A} /quiet /norestart"
Start-Process -FilePath "msiexec.exe" -ArgumentList $args -Wait -ErrorAction Stop
Write-Output "The app uninstallation successfully"
} catch {
Write-Output "The installation failed. Error: $($_.Exception.Message)"
}Using package manager to uninstall silently
If PowerShell 7 was installed via a package manager, run this command in an elevated Command Prompt or PowerShell to uninstall it silently:
# Windows Package Manager (winget)
winget uninstall --id Microsoft.PowerShell
# Chocolatey
choco uninstall -y powershell-coreMethod 5: Group Policy (GPO)
Deploying PowerShell 7 across your domain-joined Windows machines can be quick and hassle-free with the help of Group Policy. Advantages of GPO Deployment:
- Centralized management: No need to manually touch individual machines.
- Silent and automated installation: Perfect for enterprise scenarios.
- Easy to configure additional settings using Group Policy.
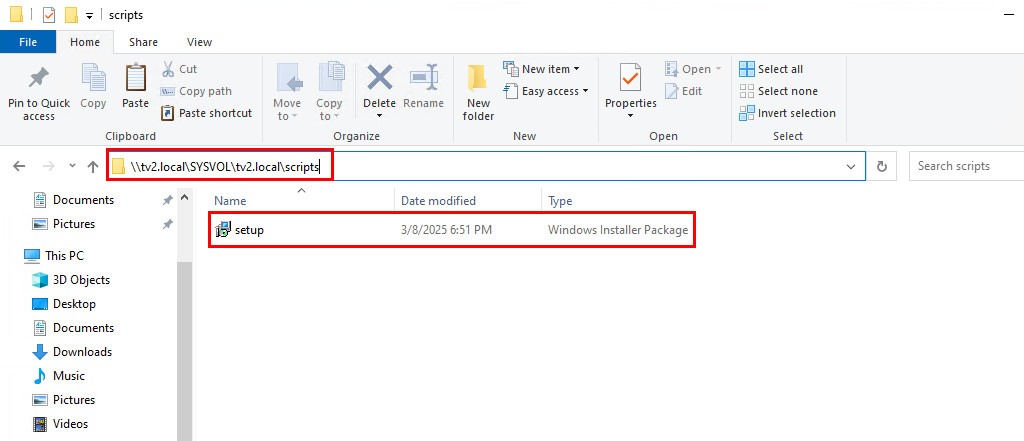
1. First, download the PowerShell 7 installer, rename it to setup.msi, and then copy it to a network-accessible shared folder that all domain computers and domain users can access.
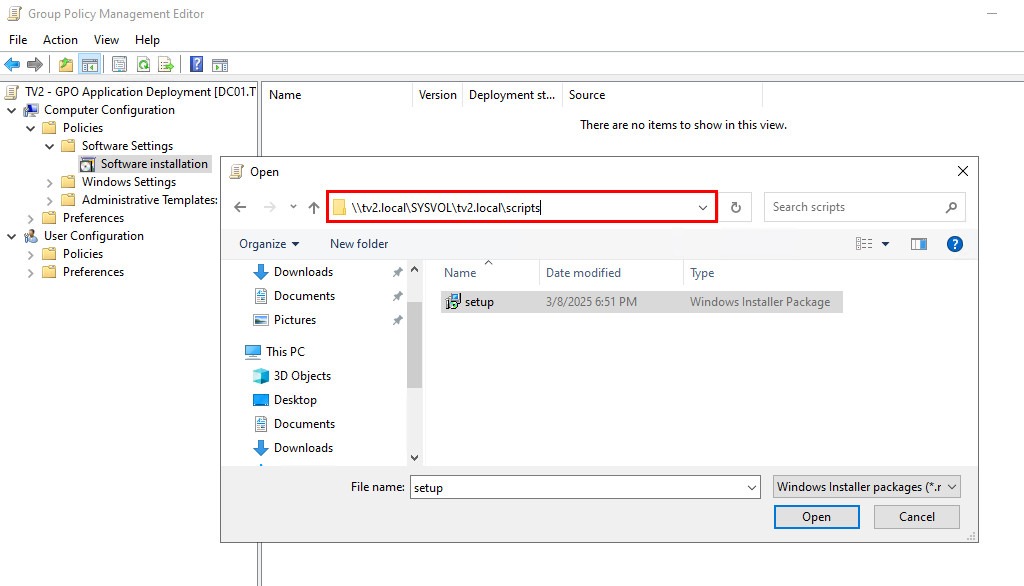
The installer can be saved on a file server. For demonstration purposes, it will be stored in \\tv2.local\SYSVOL\tv2.local\scripts. Please remember to replace tv2.local with your local domain name.
2. Next, on a domain controller, open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) then:
- Navigate to the Organizational Unit (OU) that contains the computers where you want to deploy PowerShell 7.
- Right-click the OU, and select Create a GPO in this domain, and link it here.
- Name your GPO something relevant, such as “TV2 – GPO Application Deployment”.
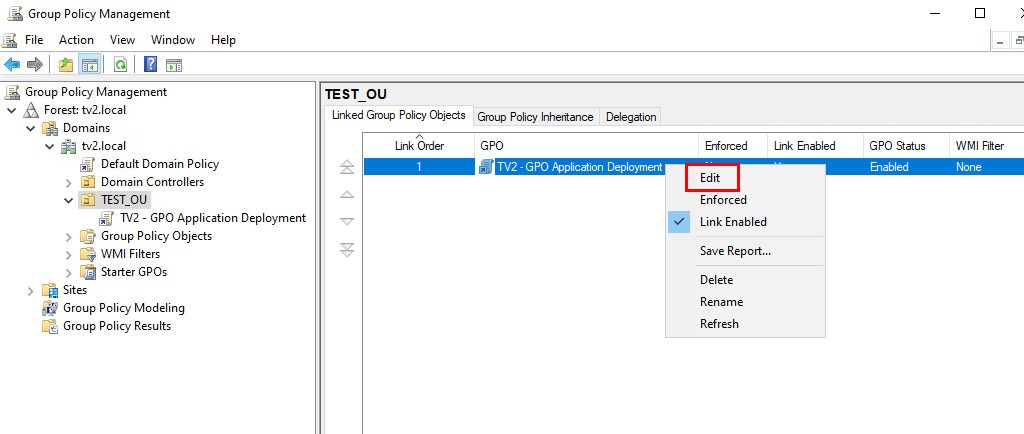
3. Next, edit the GPO by right clicking your newly created GPO and selecting Edit.
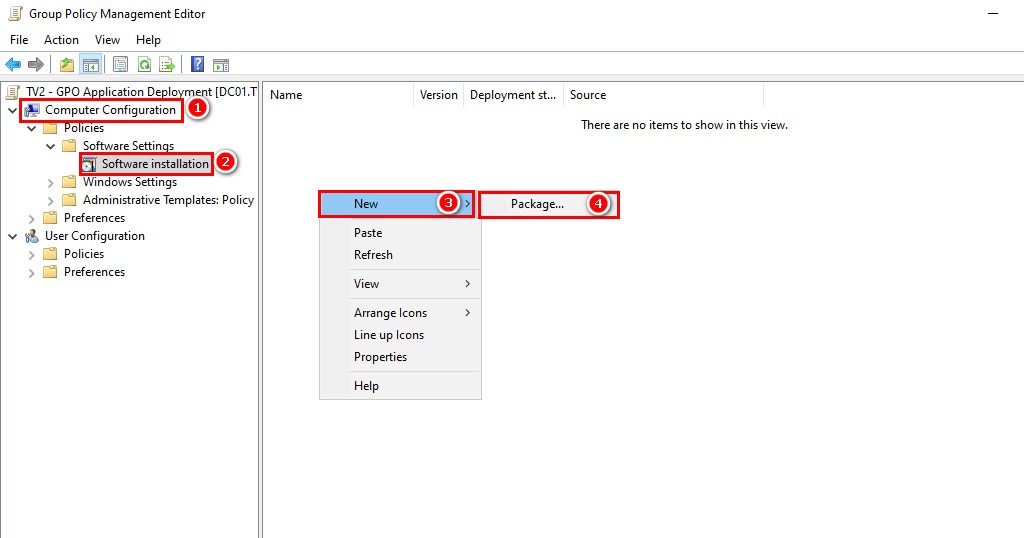
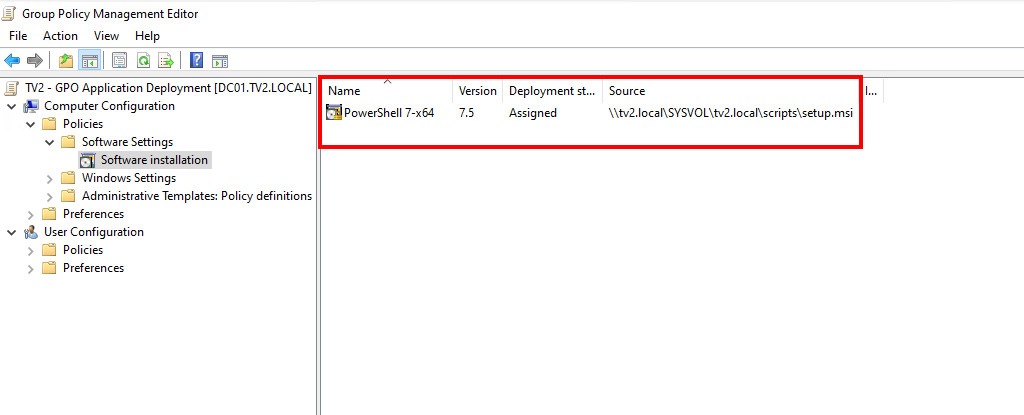
4. In the Group Policy Management Editor:
- Navigate to Computer Configuration → Policies → Software Settings → Software Installation.
- Add the software package by right-click on blank area → New → Package….
5. The next step is to enter the UNC path of the MSI installer in the network shared location that was prepared in the previous step. For example: \\tv2.local\SYSVOL\tv2.local\scripts\setup.msi
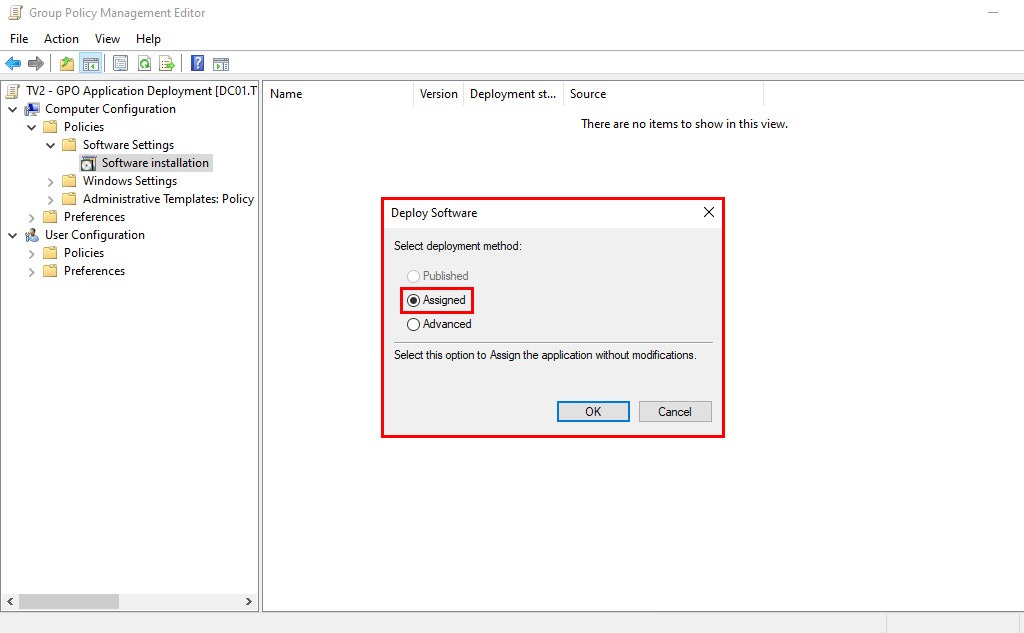
6. Select Deployment Method: In the dialog box that appears, choose Assigned (recommended for silent, system-level installations), which ensures the application installs automatically during system boot.
7. To apply the GPO immediately, on a client machine, open Command Prompt or PowerShell as an administrator and then run gpupdate /force command.
# Output
PS C:\Windows\system32> gpupdate /force
Updating policy...
Computer Policy update has completed successfully.
The following warnings were encountered during computer policy processing:
Group Policy Client Side Extension Software Installation was unable to apply one or more settings because the
changes must be processed before system startup or user logon. The system will wait for Group Policy processing
to finish completely before the next startup or logon for this user, and this may result in slow startup and
boot performance.
User Policy update has completed successfully.
For more detailed information, review the event log or run GPRESULT /H GPReport.html from the command line to
access information about Group Policy results.
Certain Computer policies are enabled that can only run during startup.
OK to restart? (Y/N)8. After applying the GPO, restart the computer. Then, check the Programs and Features or the Start Menu to confirm that PowerShell 7 is installed. Alternatively, you can run the following command to check the status of GPO applied to the computer.
gpresult /r /scope:computer# Output
PS C:\Windows\system32> gpresult /r /scope:computer
...
RSOP data for on PC-001 : Logging Mode
----------------------------------------
OS Configuration: Member Workstation
OS Version: 10.0.19045
Site Name: Default-First-Site-Name
COMPUTER SETTINGS
------------------
CN=PC-001,OU=TEST_OU,DC=tv2,DC=local
Last time Group Policy was applied: 3/8/2025 at 7:24:54 PM
Group Policy was applied from: DC01.tv2.local
Group Policy slow link threshold: 500 kbps
Domain Name: TV2
Domain Type: Windows 2008 or later
Applied Group Policy Objects
-----------------------------
TV2 - GPO Application Deployment
Default Domain Policy
The following GPOs were not applied because they were filtered out
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Local Group Policy
Filtering: Not Applied (Empty)
...Key Notes and Troubleshooting
- File Paths: Always use the UNC path ( \\tv2.local\SYSVOL\tv2.local\scripts\setup.msi ) when referencing the MSI file in Group Policy to ensure accessibility.
- Permissions: Ensure the shared installer path has proper Read permissions for Domain Computers or Authenticated Users.
- Testing: Always test your GPO on a small group of computers before applying it to the entire domain.
Installer Not Downloading: Ensure that shared folder permissions are correctly set and confirm that the UNC path is accessible from the client machines.
Group Policy Not Applied: Ensure the policy is linked to the correct OU containing client computers.
Conclusion
Silently installing PowerShell 7 on Windows offers a streamlined, efficient approach for deploying the app across multiple systems, particularly in organizational or enterprise environments. By leveraging command-line parameters, users can automate installations without disruptive interfaces, ensuring consistency and saving time. This method is especially valuable for IT administrators and system managers tasked with large-scale deployments, as it minimizes user interaction and reduces potential errors.
Not a reader? Watch this related video tutorial: