Table of Contents
Purpose of the Script
- Automatically download and install the latest version of Acrobat Reader.
- Uses Microsoft’s Winget GitHub. repository to locate the official installer.
- Performs a silent installation for all users.
# Define the GitHub API URL for the app manifests in winget-pkgs.
$apiUrl = "https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit"
# Fetch version folders then filter only version folders.
$versions = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $apiUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$versionFolders = $versions | Where-Object { $_.type -eq "dir" }
# Extract and sort version numbers to get the latest version.
$sortedVersions = $versionFolders | ForEach-Object { $_.name } | Sort-Object {[version]$_} -Descending -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$latestVersion = $sortedVersions[0]
Write-Host "Latest Adobe Acrobat Reader version: $latestVersion."
# Get contents of the latest version folder to find the .installer.yaml file.
$latestApiUrl = "$apiUrl/$latestVersion"
$latestFiles = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $latestApiUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$installerFile = $latestFiles | Where-Object { $_.name -like "*.installer.yaml" }
# Download and parse YAML content to get the Url of the latest installer file.
$yamlUrl = $installerFile.download_url
$yamlContent = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $yamlUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$null = ($yamlContent -join "`n") -match "InstallerUrl:\s+(http.*)"
$installerUrl = $Matches[1]
Write-Host "Downloading installer from: $installerUrl"
# Download the latest installer to the temp folder.
$webClient = [System.Net.WebClient]::new()
$webClient.DownloadFile($installerUrl, "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe")
# Start the install process.
Start-Process -FilePath "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe" -ArgumentList '-sfx_nu /sAll /rs /msi' -Wait
# Delete the downloaded installer file.
Remove-Item -Path "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Write-Host "Adobe Acrobat Reader installation completed."Step-by-Step Explanation
Below is a detailed explanation of what each part of the PowerShell script does. The script is designed to automatically install or update Acrobat Reader on Windows computers.
1. Define the API URL
$apiUrl = "https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit"- Points to the Acrobat Reader manifest folder in the winget-pkgs GitHub repository.
- This folder contains subfolders for each version.
2. Get the list of available versions
$versions = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $apiUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$versionFolders = $versions | Where-Object { $_.type -eq "dir" }- Fetches all items in the folder (both files and folders).
- Filters to only include directories, because each directory represents a Acrobat Reader version.
# Output
PS C:\> $versionFolders
name : 21.007.20099
path : manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/21.007.20099
sha : 541aa602a3cb1168afecf88aec8fc8b3012a0556
size : 0
url : https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/21.007.20099?ref=
master
html_url : https://github.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/tree/master/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/21.007.20099
git_url : https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/git/trees/541aa602a3cb1168afecf88aec8fc8b3012a0556
download_url :
type : dir
_links : @{self=https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/21.007.200
99?ref=master;
git=https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/git/trees/541aa602a3cb1168afecf88aec8fc8b3012a0556;
html=https://github.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/tree/master/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/21.007.20099}
...3. Extract and sort versions
$sortedVersions = $versionFolders | ForEach-Object { $_.name } | Sort-Object {[version]$_} -Descending -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$latestVersion = $sortedVersions[0]- Extracts folder names (version numbers).
- Sorts them as version objects (not strings) in descending order.
- Picks the latest version (first in the sorted list).
# Output
PS C:\> $sortedVersions
25.001.20577
25.001.20566
25.001.20531
25.001.20521
25.001.20474
25.001.20458
25.001.20435
25.001.20432
25.001.20428
24.005.20421
24.005.20414
24.005.20399
24.005.20392
...4. Get the .installer.yaml file for the latest version
$latestApiUrl = "$apiUrl/$latestVersion"
$latestFiles = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $latestApiUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$installerFile = $latestFiles | Where-Object { $_.name -like "*.installer.yaml" }- Looks inside the latest version folder.
- Finds the *.installer.yaml file, which contains metadata about the installer (URLs, architecture, etc.).
# Output
PS C:\> $installerFile
name : Adobe.Acrobat.Reader.64-bit.installer.yaml
path : manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/25.001.20577/Adobe.Acrobat.Reader.64-bit.installer.yaml
sha : f42c5a63643b69dd0620d553c4b68e55cd758d31
size : 2327
url : https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/25.001.20577/Adob
e.Acrobat.Reader.64-bit.installer.yaml?ref=master
html_url : https://github.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/blob/master/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/25.001.20577/Adobe.Acrob
at.Reader.64-bit.installer.yaml
git_url : https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/git/blobs/f42c5a63643b69dd0620d553c4b68e55cd758d31
download_url : https://raw.githubusercontent.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/master/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/25.001.20577/A
dobe.Acrobat.Reader.64-bit.installer.yaml
type : file
_links : @{self=https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/25.001.205
77/Adobe.Acrobat.Reader.64-bit.installer.yaml?ref=master;
git=https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/git/blobs/f42c5a63643b69dd0620d553c4b68e55cd758d31; html=https
://github.com/microsoft/winget-pkgs/blob/master/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit/25.001.20577/Adobe.Acrobat.Re
ader.64-bit.installer.yaml}5. Extract installer URLs from YAML to find the URL of the latest version
$yamlUrl = $installerFile.download_url
$yamlContent = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $yamlUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$null = ($yamlContent -join "`n") -match "InstallerUrl:\s+(http.*)"
$installerUrl = $Matches[1]- Downloads the YAML file as raw text.
- Extracts all InstallerUrl entries using regular expressions.
- Picks the URL using an index number.
# Output
PS C:\> $installerUrl
https://ardownload2.adobe.com/pub/adobe/acrobat/win/AcrobatDC/2500120577/AcroRdrDCx642500120577_MUI.exe6. Download the installer
$webClient = [System.Net.WebClient]::new()
$webClient.DownloadFile($installerUrl, "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe")- Downloads the installer to the Windows temp folder ($Env:Temp)
7. Install Acrobat Reader silently
Start-Process -FilePath "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe" -ArgumentList '-sfx_nu /sAll /rs /msi' -Wait- Runs the installer in silent mode, no user interaction.
8. Clean up the installer and notify to user
Remove-Item -Path "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Write-Host "Adobe Acrobat Reader installation completed."- Deletes the installer after installation to keep the system clean.
- Outputs a message to confirm the installation status.
How to install using PowerShell
To install the app, simply open PowerShell as an administrator, copy the code snippets below, paste them into the PowerShell window, and press .
# Define the GitHub API URL for the app manifests in winget-pkgs.
$apiUrl = "https://api.github.com/repos/microsoft/winget-pkgs/contents/manifests/a/Adobe/Acrobat/Reader/64-bit"
# Fetch version folders then filter only version folders.
$versions = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $apiUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$versionFolders = $versions | Where-Object { $_.type -eq "dir" }
# Extract and sort version numbers to get the latest version.
$sortedVersions = $versionFolders | ForEach-Object { $_.name } | Sort-Object {[version]$_} -Descending -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$latestVersion = $sortedVersions[0]
Write-Host "Latest Adobe Acrobat Reader version: $latestVersion."
# Get contents of the latest version folder to find the .installer.yaml file.
$latestApiUrl = "$apiUrl/$latestVersion"
$latestFiles = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $latestApiUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$installerFile = $latestFiles | Where-Object { $_.name -like "*.installer.yaml" }
# Download and parse YAML content to get the Url of the latest installer file.
$yamlUrl = $installerFile.download_url
$yamlContent = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $yamlUrl -Headers @{ 'User-Agent' = 'PowerShell' }
$null = ($yamlContent -join "`n") -match "InstallerUrl:\s+(http.*)"
$installerUrl = $Matches[1]
Write-Host "Downloading installer from: $installerUrl"
# Download the latest installer to the temp folder.
$webClient = [System.Net.WebClient]::new()
$webClient.DownloadFile($installerUrl, "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe")
# Start the install process.
Start-Process -FilePath "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe" -ArgumentList '-sfx_nu /sAll /rs /msi' -Wait
# Delete the downloaded installer file.
Remove-Item -Path "$env:TEMP\Adobe.Acrobat.Reader-latest.exe" -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Write-Host "Adobe Acrobat Reader installation completed."Installing using a PowerShell script
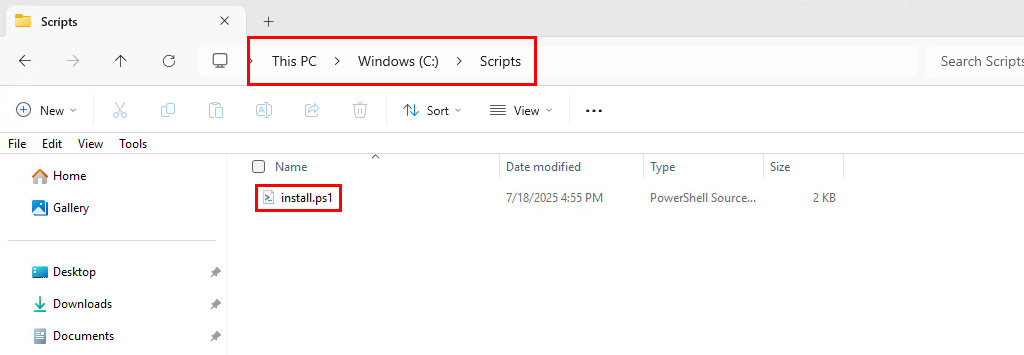
Alternatively, you can create a PowerShell script using the code snippet above. For instance, I’ve created and save a script at “C:\Scripts\install.ps1″.
Next, open PowerShell (or Terminal) as an administrator and execute the PowerShell script using either the call operator or dot notation.
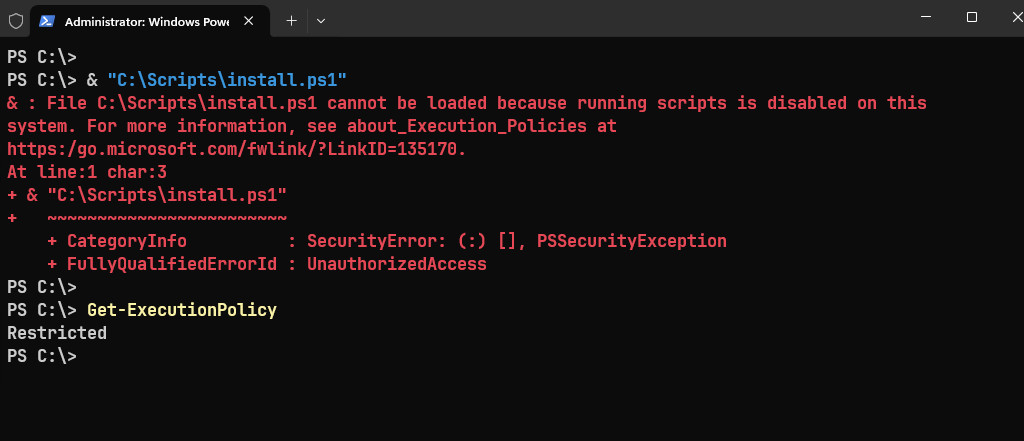
& "C:\Scripts\install.ps1"# Output
PS C:\> & "C:\Scripts\install.ps1"
Latest Adobe Acrobat Reader version: 25.001.20577.
Downloading installer from: https://ardownload2.adobe.com/pub/adobe/acrobat/win/AcrobatDC/2500120577/AcroRdrDCx642500120577_MUI.exe
Adobe Acrobat Reader installation completed.PowerShell execution policy
Root cause: The Windows PowerShell execution policy is designed to block untrusted scripts from impacting your Windows client environment. These policies act as security settings that define the trust level for scripts executed in PowerShell. On client operating systems, the default execution policy is set to Restricted, which stops Windows PowerShell commands and scripts from running.
To fix the issue, adjust the execution policy by running the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSignedYou’ll encounter a security risk warning. Enter “A” when prompted to continue.
PS C:\> Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Execution Policy Change
The execution policy helps protect you from scripts that you do not trust. Changing the execution policy
might expose you to the security risks described in the about_Execution_Policies help topic at
https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170. Do you want to change the execution policy?
[Y] Yes [A] Yes to All [N] No [L] No to All [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "N"): A
PS C:\>
PS C:\> Get-ExecutionPolicy
RemoteSignedUse Cases
- Automated software deployment
- Scheduled automatic updates
- Silent install for non-technical users
- Alternative to winget or manual downloads